What is Sex Linkage?

Thomas H. Morgan, in 1910, with his experiments on the Drosophila fruit fly came across these genes that are specifically linked to the sex determining chromosomes of organisms. Therefore, these genes would inherit with the sex chromosomes resulting in the vivid phenotypic variations that we see between the different sexes of various organisms but also diseases.
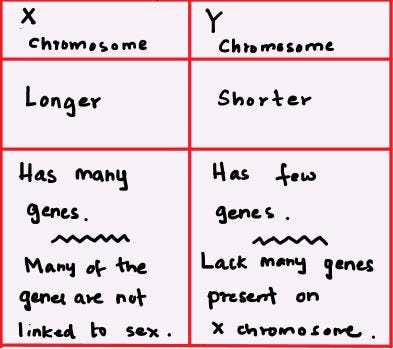 |
| X and Y Chromosomes of Humans |
What are sex chromosomes?
In humans, we have 23 pairs of chromosomes in every single living cell of our body. The 23rd pair is called the sex chromosome pair, which determines whether you are a female or a male. The XX sex chromosome pair result in a female while the XY pair result in a male.
In addition to sex determination, they also contain genes that express several male and female traits and traits not related to sex.
What are sex linked genes?
Genes that are linked to the sex chromosomes in organisms are called sex linked genes.
Sex linked genes can be found in either the X or Y chromosome. If it is found in the X chromosome, it is called X-linked. X-linked genes are only inherited with the X sex chromosome, this is called X-linked inheritance. The genes found in the Y chromosome are called Y-linked. Y-linked genes are only inherited with the Y chromosomes, this is called Y-linked inheritance. The Y-linked genes are also referred to as Holandric genes. Y-linked genes are only inherited from the father to the son and never to the daughter.
X-linked genes are phenotypically expressed in both males and females while holandric or Y-linked genes are only expressed in males.
How can X and Y-linked inheritance be identified?
An analysis of pedigree chart which documents the family history and their relationships can be carried out to easily identify such an inheritance.
X-linked traits are mostly recessive while there are a few dominant traits. X-linked recessive traits have a higher probability of phenotypically expressing in males than females. A X-linked dominant trait is expressed more frequently in females.(Why?)
X-linked traits exhibit specific patterns of inheritance, 2 inheritance patterns of a X-linked recessive trait is shown below,
- Skip-generation pattern; this is the pattern observed when a certain trait is not expressed in one generation but expressed in the one before and the one after i.e., it has skipped one generation.
- Criss-cross pattern; this pattern is observed when a certain trait is inherited from the father to his daughter in one generation and from her to his son in the next generation. Here, the daughter acted as the carrier. Those that have a heterozygous genotype carry the gene to the next generation without expressing it themselves.
The above 2 patterns is represented in the below image,
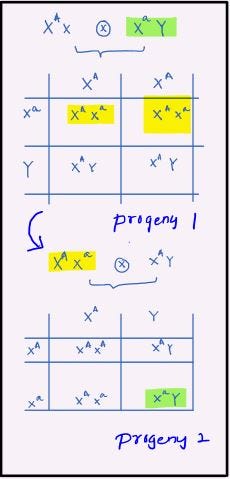 |
| Inheritance of a X-Linked Recessive Trait |
[Green highlight — phenotypically expressed, Yellow highlight — not phenotypically expressed]
What are the types of X-linked inherited disorders?
X-linked recessive disorders
- Muscular Dystrophy
- Hemophilia
- Red-Green Color Blindness
- MASA syndrome
- XMEN Disease (Nothing to do with mutants)
X-linked dominant disorders
- Rett syndrome
- Double-cortex syndrome
Y chromosomes only have a few genes, the SRY gene (Sex determining Region Y) and genes involving in sperm production.
What are Incompletely Sex Linked Genes?
Genes that are found in both the X and Y chromosomes are Incompletely Sex Linked.








Comments
Post a Comment